Adhesive tape systems offer great potential to streamline industry workflows. The right choice of backing material and adhesive in relation to the application is important.
CMC Klebetechnik has been coating technical films, fabrics and nonwovens with adhesives for over 60 years. Due to the wide range of substrates and adhesives, the adhesive tapes can be used in all industrial sectors. For customers who have special requirements, CMC Klebetechnik develops customized solutions (contract coating, contract development, coating to order).
All our adhesive tapes are manufactured according to strict quality regulations and are subject to continuous control. Many adhesive tapes are listed by UL under E93622. CMC Klebetechnik has been certified according to ISO 9001 since 1995.
Our product portfolio contains more than 200 different technical films and technical adhesive tapes. You will find our products and further information on these different CMC types on the following pages. We will support you in selecting the right adhesive tape for your application.
Weitere Informationen zu den Basisfolien
Explanations and definitions of our materials
Polyester (PET)/ CMC 10xxx/12xxx
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Du Pont, Mylar® A |
E93687 |
1 |
UL 94 VTM-2 / HWI= 5 | B |
| Mitsubishi, Hostaphan® RN |
E53895 |
1* |
not measured at 23µm/ 50µm UL 94 VTM-2 | B |
Polycarbonat (PC)
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Covestro, Makrofol® EN |
E168120 | 3** | UL 94 VTM-2 | B |
Polyethylene naphthalate (PEN) / CMC 61xxx = PEN
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Toyobo Film Solutions Limited™ (formerly of Teijin), Teonex®. | E51743 | 3* | UL 94 VTM-2 | F |
Polyetherimid (PEI)
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Sabic, Ultem® | E103380 | 4 | UL 94-V0 (from 50µm) | F |
Perflourethylene propylene (FEP)
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Saint Gobain, Norton FEP | E311412 | 1* |
UL 94-V0 ** |
F |
Polyaramid-Papier / CMC 65xxx = Nomex
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Du Pont, Nomex® 410, 411, E 56A | E34739 | - | UL 94-V0/ HWI=0 |
H |
Polyimide (PI) / CMC 70xxx = Kapton
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Du Pont, Kapton® HN, MT | E39505 | 4 |
UL 94-V0/ HWI=0 |
H |
Polyetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) / CMC 75xxx = PTFE
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Du Pont, Teflon® | 1 |
|
H |
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Victrex, Aptiv™ | E161131 | 4 |
UL 94 V1 (from 50µm) | H |
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)
|
Manufacturer and trade name |
UL file |
CTI |
Flammability (also DIN 60454) |
Thermal class/ Insulation class |
| Toray, Torelina® | E86423 | 3 | UL 94 V0 | H |
*): CTI value not specified in UL file or not tested by UL
(**): Values apply to the raw material, no specification in UL file
Explanation: Polyester films are usually listed at 105°C (generic value) - Class B for adhesive tapes results from the corresponding tests for adhesive tapes. All films can withstand higher temperatures in the short term (e.g. polyester up to approx. 200°C for hours). The insulating material class specifications refer to long-term application as insulating film in electrical engineering
CTI= tracking resistance 0= >600V (only CMC 278xx, Formex) 1= >400V-600V (e.g. polyester film like Hostaphan or Mylar, Teonex, Kapton FN). 2= >250V-400V 3= >175V-250V (e.g. Aptiv Peek, Nomex) 4= >100V-175V (e.g. Kapton HN) |
HAI= High Arc Ignition ; 1= 60-120 2= 30-60 3= 15-30 4= 0-15 |
HWI= Hot Wire Ignition, glow wire test; |
Comparison of properties of plastic
|
Features |
Test method |
Unit |
PEN |
PI |
PEI |
PPS |
PET |
| Tensile strength |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Elongation at break |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Continuous operating temperature (mech. acc. to UL Yellow Card) |
UL-746B |
°C |
160 |
200 |
170 |
180 |
105 |
| Continuous operating temperature (electr. acc. to UL Yellow Card) |
UL-746B |
°C |
180 |
240 |
180 |
180 |
105 |
| Glass transition temperature (film) |
TDFJ method by DMA |
°C |
155 |
- |
212 |
90 |
110 |
| Melting point |
DSC |
°C |
269 |
- |
- |
2855 |
258 |
| Breakdown voltage |
JIS C-2318 |
kv/mm |
300 |
280 |
140 |
320 |
280 |
| Dielectric constant |
JIS C-2318 |
- |
2,9 |
3,3 |
3,2 |
28 |
3,1 |
| Water intake |
TDFJ method |
% |
0,3 |
1,3 |
0,3 |
0,02 |
0,4 |
| Density |
JIS C-2151 |
g/cm³ |
1,36 |
1,43 |
1,27 |
1,35 |
1,40 |
| Flammability |
UL-94 |
|
VTM-2 |
V-0 |
V-0 |
VTM-0 |
VTM-2 |
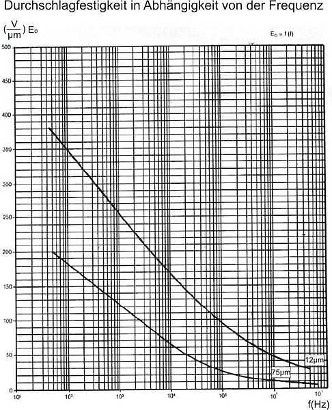
Breakdown voltage versus
The dielectric strength of polymers changes with frequency, since the increasingly rapid repolarization effects lead to losses in the material. As an example, the change is shown here using the example of polyester film with 12µm and 75µm. With a 12µm thick PET film, the breakdown voltage is reduced by a factor of 8 compared with "normal" 50/60Hz operation. However, these values cannot simply be transferred to other plastics.
Relative dielectric constant (permittivity) of different materials
For applications requiring particularly high corona resistance, there is Nomex 418 and Kapton CR. Both products achieve highest resistance by adding inorganic insulation materials. Please inquire if you need these films self-adhesive. Due to the small difference of the εr of PTFE and FEP compared to air, these films are especially suitable for partial discharge sensitive assemblies. In addition, the temperature resistance is very good, resulting in a lower temperature influence on the PD insertion voltage.
| Nomex 410 |
60 Hz / 100 kHZ |
1.6 (50µm, 80µm) / 1.8 |
| Teonex (PEN) |
60 Hz |
3,24 |
| Kapton (PI) |
1 kHZ |
3,9 |
| PTFE and FEP |
Frequency independent |
2,1 |
| Polyester (PET) |
50 Hz / 1 MHz |
3,3 / 3,0 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) |
50 Hz |
3,0 |
| Polypropylene (PP) |
50 Hz |
2,4 |
| Polyethylene (PE) |
50 Hz |
2,1 |
| FR4 |
50 Hz |
4,3 - 5,4 |
| Kapton MT |
60 Hz |
4,2 |
Water vapor permeability of various films
In many cases, the permeability to water vapor depends on parameters such as film thickness, difference in humidity and temperature. However, some engineering plastics are more suitable as vapor barriers than others. The graph represents a rough guide in terms of water vapor permeability per square meter per day in grams of water.
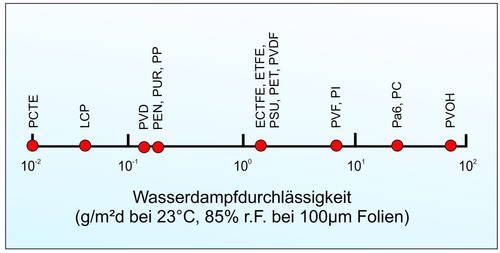
Comparison of engineering plastics
|
Material |
Glass transition temperature |
Melting point |
Modulus of elasticity |
Density |
Thermal conductivity |
| Polyphenylene sulfides (PPS) |
85 to 95 °C | 285 to 290 °C | 3700 MPa | 1.34 to 1.36 g/cm³ | (na) W /(m-K) |
| Polysulfones (PSU) | 185 to 190 °C |
|
2500 to 2700 MPa | 1.24 to 1.25 g/cm³ | 0.15 W / (m-K) |
| Polyetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | 125 to 130 °C | 325 to 330 °C | 400 to 750 MPa | 2.13 to 2.23 g/cm³ | 0.23 to 0.25 W / (m-K) |
| Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) | 40 °C | 170 to 175 °C | 2000 to 2900 MPa | 1.76 to 1.78 g/cm³ | 0.19 W / (m-K) |
| Tetrafluoroethylene / hexafluoropropylene copolymer (FEP) | (na) °C | 253 to 282 °C | 350 MPa | 2.12 to 2.17 g/cm³ | 0.25 W / (m-K) |
| Ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) | (na) °C | 225 to 275 °C | 1100 MPa | 1.7 g/cm3 | 0.23 W / (m-K) |
| Polyvinyl fluoride (PVF) | -20 to +40 °C | 195 to 200 °C | 2100 to 2600 MPa | 1.37 to 1.39 g/cm³ | (na) W / (m-K) |
| Polyamide 6-3-T (PA6-3T) |
149 to 153 °C |
|
2000 MPa | 1.12 g/cm³ | 0.23 W / (m-K) |
| Polyamide 6/6T (PA6/6T) | 60 to 100 °C | 250 to 300 °C | 3500 to 3600 MPa | 1.18 g/cm³ | (na) W / (m-K) |
| Polyetherimides (PEI) | 215 to 230 °C |
|
2900 to 3000 MPa | 1.27 g/cm³ | 0.22 W / (m-K) |
| Polyethersulfones (PES) | 225 to 230 °C |
|
2600 to 2800 MPa | 1.37 g/cm³ | 0.18 W / (m-K) |
| Polyetheretherketones (PEEK) | 145 °C | 335 °C | 3700 MPa | 1.32 (semi-cr) 1.27 (am) g/cm³ |
0.25 W / (m-K) |
| Polyacryletherketoneetherketoneketones (PEKEKK) | 165 to 175 °C | 380 to 390 °C | 4300 MPa | 1.3 g/cm³ | 0.29 W / (m-K) |
| Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) | (na) °C | 302 to 306 °C | 800 MPa | 2.14 to 2.16 g/cm³ | (na) W / (m-K) |
Impregnant compatibility of the adhesive
The following resins were tested: vinyl toluene-based (e.g. Voltatex 4130), acrylate-based (e.g. Voltatex 4200), styrene-based (e.g. Voltatex 4001).
| CMC adhesive tape | Result |
| CMC 10260 | Very good compatibility |
| CMC 65100 | Very good compatibility |
| CMC 65120 | Very good compatibility |
| CMC 17719 | Very good compatibility |
| CMC 16701 | Very good compatibility* |
| CMC 16100 | Very good compatibility* |
| CMC 10966 (yellow, colorless) | Very good compatibility |
The test was performed as follows:
The adhesive tape was applied to a metal sheet a.) with the adhesive facing the metal sheet and b.) with the adhesive side facing outward. Dipping time in test resin 10 minutes and dripping time 10 minutes.
Visual inspection of the adhesive tape sample and the impregnating agent (e.g. discoloration and swelling).
Then curing of the specimen at 150°C/60 min.
Subsequently, adhesion and tackiness of the two test specimens were evaluated. A general slight to strong tackiness *) was found (adhesive to the outside) when using acrylate-based resins, but this did not affect the function per se.
The influence of the gelling properties after 480 hours was consistently very positive and hardly measurable